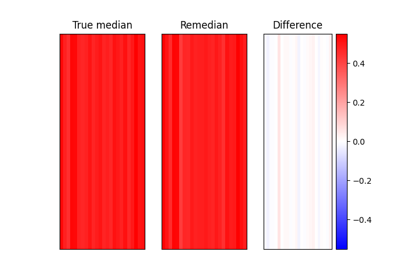
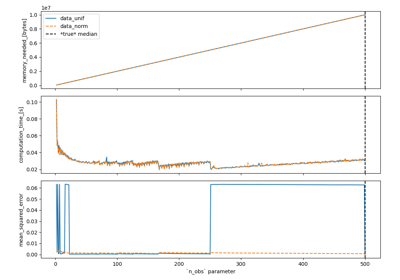
remedian.Remedian¶
- class remedian.Remedian(obs_size, n_obs, t)[source]¶
Remedian object for a robust averaging method for large data sets.
Implementation of the Remedian algorithm, see [1] [2] [3] for references. This algorithm is used to approximate the median of several data chunks if these data chunks cannot (or should not) be loaded into memory at once. See “Notes” section for further information.
- Parameters:
- obs_size
ndarray The shape of each data chunk (=observation) to be fed into the Remedian object.
- n_obs
int The number of observations to be stored within each array. If n_obs >= t, Remedian will equal the median. The smaller this parameter, the fewer data have to be loaded into memory at once, but the less accurate the approximation of the median will be.
- t
int The total number of observations from which a median should be approximated.
- obs_size
Notes
Given a data chunk of size obs_size, and t data chunks overall, the Remedian class sets up a number k_arrs of arrays of length n_obs.
The median of the t data chunks of size obs_size is then approximated as follows: One data chunk after another is fed into the n_obs positions of the first array. When the first array is full, its median is calculated and stored in the first position of the second array. After this, the first array is re-used to fill the second position of the second array, etc. When the second array is full, the median of its values is stored in the first position of the third array, and so on.
The final “Remedian” is the median of the last array, after all t data chunks have been fed into the object.
In other words, given an n-dimensional array, the Remedian class approximates the median of this array across the ith dimension and you have to break up your n-dimensional array into t n-1-dimensional arrays that are given to Remedian one after another.
References
[1]P.J. Rousseeuw, G.W. Bassett Jr., “The remedian: A robust averaging method for large data sets”, Journal of the American Statistical Association, vol. 85 (1990), pp. 97-104
[2]M. Chao, G. Lin, “The asymptotic distributions of the remedians”, Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, vol. 37 (1993), pp. 1-11
[3]Domenico Cantone, Micha Hofri, “Further analysis of the remedian algorithm”, Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 495 (2013), pp. 1-16
- Attributes: